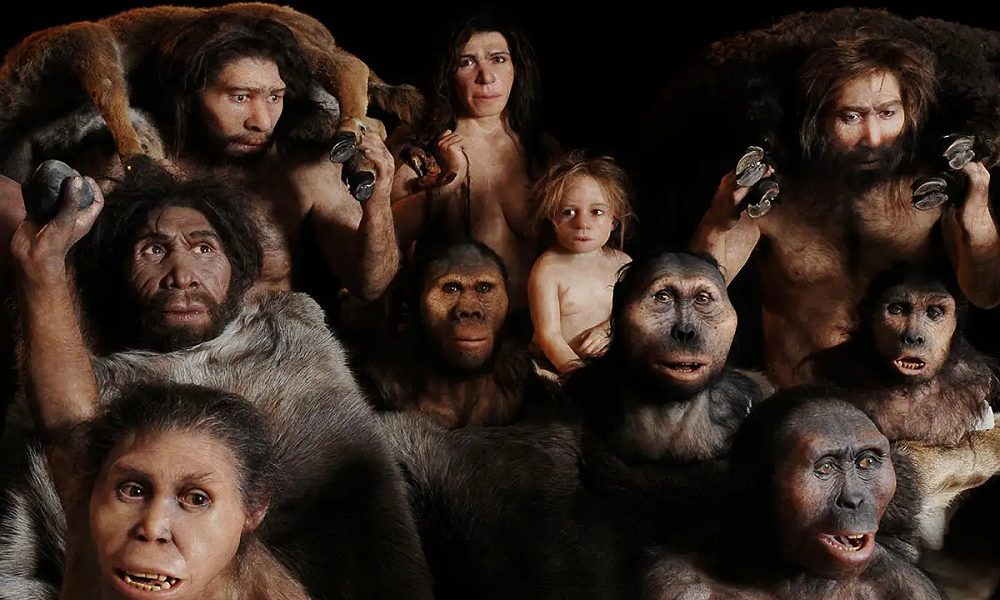

The Story Of Humanity’s Origins Explained Through The Discoveries Of Fossil Fuels

As it turns out, we know surprisingly little about human origins and evolution, but results from fossils and human DNA analysis have given us an idea of the evolution of Homo Sapiens some 300,000 years ago. The term Homo Sapiens is derived from the Latin dictionary, which means “wise man.” This term was applied in 1758 by Carlus Linnaeus, one of the fathers of modern biological classifications, but before that, humans were classified as primates.
The human framework vastly differs from the framework used for the rest of nature, but Linnaeus faced difficulty in distinguishing Homo Sapiens from apes, specifically in physical terms. Since Carlus’s time, a large fossil record has been collected, and DNA analyses have been performed with every fossil discovery.

HOP/ Stock Image | Human evolution is the lengthy process of change
The story of humans got increasingly complex, and their genomes became rich tapestries of interwoven ancestries. Modern humans are now products of the sprawling history of shifts, dispersal, separation, and reunions. Their history is vastly characterized by diversity, movement, and a mixture of decades.
Fascinating findings of human intelligence
In 2021, researchers investigated all kinds of collected fossils, such as ancient skulls, to study the evolution of human brains. They found out that early human brains were very similar to ape brains. In fact, their brains didn’t develop until 1.5 to 1.7 million years. The endocasts’ results revealed that the brain’s frontal lobe took a long time to develop in humans and process cognitive tasks.
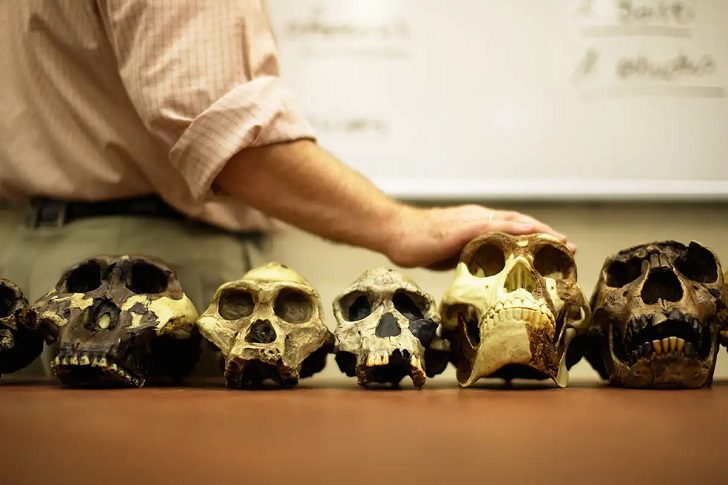

DonSmith/ Alamy | The story of human evolution is a complicated one
The first brain was discovered about 300,000 years ago in Africa, and these brains were much larger than our brains. The brain shape modernized about 100,000 years after that. Fossil records and human DNA have shown that our ancestors were connected to many African clans and lived 260,000 to 350,000 years ago. This is where modern humans inherited their fundamental commonalities and behavior.
These behaviors unite both modern and ancient humans. For example, ancient caves represented art with paintings, drawings, and idols, and they used their creativity to make projectile weapons such as bows and spears. Similarly, modern humans sing, dance, make art, tell stories and form multigenerational social groups with bonds between men and women to care for their children.
Other findings relative to human origins
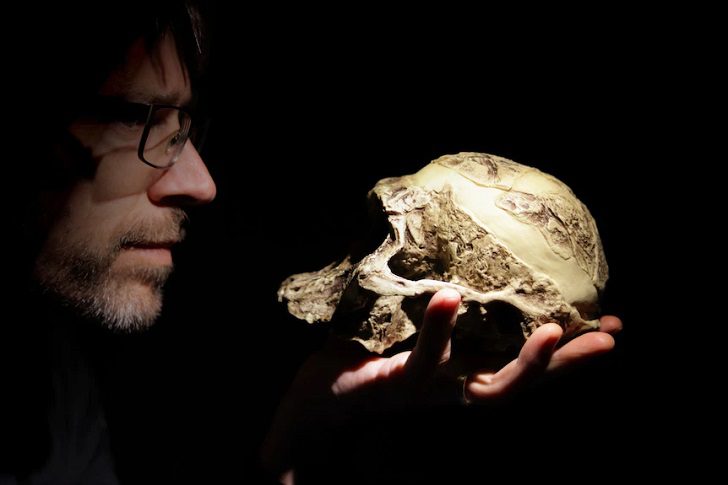

Getty Images/ Ivan Mattioli | There’s something about human evolution that’s inherently intriguing
The “Descent of Man” and “On the Origin of Species,” published by Charles Darwin in 1871 and 1859 respectively, pointed out the similarities between humans and African apes such as gorillas, chimpanzees, orangutans, and gibbons. Since DNA molecules are relatively weak molecules compared to other biomacromolecules, experts disagree about Neandertal bones and their origins.
But the discovery has also led to the discovery of a new species in China called the Dragon man. The findings are still controversial, but the fossil is a roughly 146,000-year-old skull and the largest Homo skull on record yet. Homo Bodoensis is another possible direct ancestor of Homo Sapiens that date back to 775,000 to 130,000 years, but their lineage has not yet left any traces around the world.
More in Lifestyle
-
`
How to Become a Property Manager in 6 Easy Steps
So, you are wondering how to become a property manager? If you love real estate and have a knack for organization,...
July 17, 2024 -
`
Everything You Need to Know About Aerobic Threshold
When you start to exercise, you may have wondered, What is an aerobic threshold? This term is key to understanding how...
July 12, 2024 -
`
What Is the Best Time to Visit Yellowstone?
May is the Best Time to Visit Yellowstone First up: May is often considered one of the best times to visit...
July 2, 2024 -
`
Jesse Plemons Opens Up About Being Matt Damon’s Look-Alike Actor
In the realm of Hollywood, resemblances between actors often become a point of intrigue and conversation. For Jesse Plemons, his ongoing...
June 25, 2024 -
`
5 Easy Ways of Making Money By Playing Video Games
Have you ever wondered how to make money playing video games? Imagine turning your favorite pastime into a lucrative side hustle...
June 19, 2024 -
`
What Are the Symptoms of Unbalanced pH Levels in the Body?
Our bodies are designed to maintain a delicate pH balance, ensuring that bodily fluids are neither too acidic nor too alkaline....
June 13, 2024 -
`
Inspiring Female Deep Meaningful Tattoos Ideas
Tattoos have transcended their rebellious roots and become a powerful form of self-expression. For many women, they are more than just...
June 4, 2024 -
`
Taylor Swift’s Breakup Songs: Which Ones Are the Best?
Taylor Swift has an unparalleled gift for capturing the raw emotions of love and loss in her music. Her breakup songs,...
May 29, 2024 -
`
How to Get Rid of Shin Splints? 5+ Effective Ways for Relief
Shin splints can be a real pain—literally. This common overuse injury often affects runners, military recruits, dancers, and athletes who engage...
May 23, 2024














You must be logged in to post a comment Login