
The Effect of Stress on Health

Stress is an integral part of human life. Everyone experiences stress related to work, finances, relationships, or health, but it can be beneficial as it motivates us to take action and achieve our goals. However, chronic stress can lead to several adverse health consequences, both physical and mental.
That being said, here are various effects of stress on the human body and mind.
Cardiovascular Health
When we experience stress, our body releases hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, constricting blood vessels and raising blood pressure and heart rate. If this response continues for an extended period, it can increase the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Studies have shown that individuals who experience chronic stress have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular problems than those who do not.
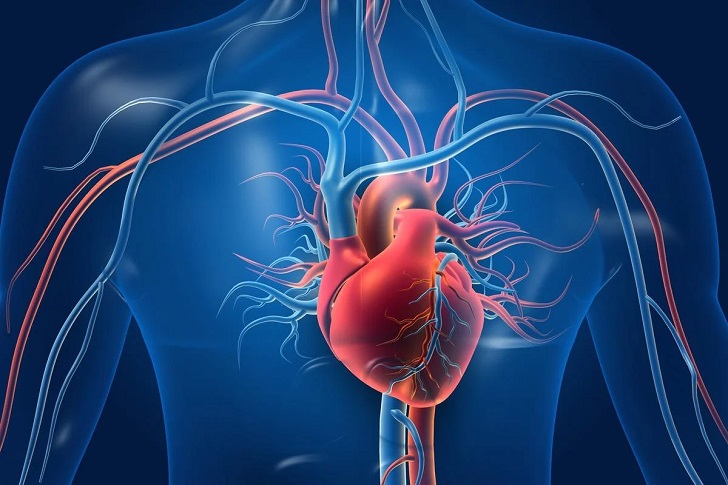
Explode/ Shutterstock | Worry and stress affects the circulation, the heart, the glands, and the whole nervous system
Digestive Health
Stress can affect the digestive system in several ways. Stress hormones slow digestion and reduce blood flow to the digestive tract, causing indigestion, bloating, and constipation. Chronic stress can lead to more severe digestive issues, such as acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Immune System Function
Stress can weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and illnesses. The stress hormone cortisol suppresses the immune system’s response to pathogens, making it harder for our body to fight infections. Studies have shown that long-term stress can reduce the production of disease-fighting white blood cells, leading to frequent illnesses and infections.
Mental Health
Chronic stress can affect our mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Stressful life events, such as job loss, divorce, or the death of a loved one, can trigger mental health disorders. Stress can also exacerbate preexisting mental health conditions, making them worse.

Shutterstock/ iStock | Stress may increase how often you get sick
Sleep Disturbances
Stress often goes hand in hand with sleep disturbances. Racing thoughts, worry, and anxiety can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. Sleep deprivation or poor-quality sleep can have profound effects on health.
It can weaken the immune system, impair cognitive function, and increase the risk of developing chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Developing healthy sleep habits and effectively managing stress can improve sleep quality and well-being.
Hormonal Imbalances
Stress can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body. Chronic stress can affect the production and regulation of cortisol, adrenaline, and insulin hormones. Hormonal imbalances can contribute to various health issues, including weight gain or loss, menstrual irregularities, fertility problems, and decreased libido. Managing stress levels is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and overall health.

Jackie Baxter Roberts/ Getty Images | When stress becomes overwhelming and prolonged, the risks for mental health problems and medical problems increase
Mental Well-being
Beyond mental health disorders, stress can significantly impact overall mental well-being. Chronic stress can lead to feelings of overwhelm, burnout, and a decreased sense of life satisfaction.
It can affect relationships, work performance, and personal fulfillment. It is essential to recognize the impact of stress on mental well-being and prioritize self-care and stress management techniques to promote a healthy and fulfilling life.
More in Medicare
-
`
What to Do in Ubud, Bali – Top Attractions & Activities
Ubud, the cultural heart of Bali, offers an array of activities that capture the essence of this enchanting island. From exploring...
September 11, 2024 -
`
Important Aspects of Your Health You Should Pay Attention To
When thinking about your health, it’s crucial to consider the key factors that create a solid foundation for your well-being. These...
September 6, 2024 -
`
6 Creative Birthday Party Ideas For Adults
Gone are the days when birthdays were just about cakes and candles. Now, it is all about creating memorable experiences that...
August 28, 2024 -
`
Are Chanel and Johnny leaving Days of Our Lives? Here Are the Facts
Fans of Days of Our Lives have been on the edge of their seats, wondering if Chanel and Johnny are leaving...
August 20, 2024 -
`
How Much Does Massage Business Make? A Profitability Breakdown
Curious about how much does massage business make? The massage spa industry in the United States is a significant sector, with...
August 14, 2024 -
`
How to Stay Healthy During Cold and Flu Season
Cold and flu season can be a daunting time, with the risk of illness looming large. Missing work, classes, or social...
August 9, 2024 -
`
Which US Virgin Island Is the Best for Your Dream Vacation
Choosing the perfect island for your dream vacation can be challenging, but each of the U.S. Virgin Islands offers something unique...
July 31, 2024 -
`
Is Taylor Swift ‘Officially’ Engaged to Travis Kelce?
Is Taylor Swift engaged to Travis Kelce? This question has been buzzing around fans lately. Well, their relationship has been nothing...
July 23, 2024 -
`
How to Become a Property Manager in 6 Easy Steps
So, you are wondering how to become a property manager? If you love real estate and have a knack for organization,...
July 17, 2024














You must be logged in to post a comment Login